Theory of Motivation for Employee Relation
What is the meaning of motivation?
“Motivation refers to the process by which a person’s efforts are energized, directed, and sustained toward attaining a goal” (Robbins and Coulter, 2016).
There are three key elements. They are,
Energy
Direction
Persistence
“Motivation as the processes that account for an individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining a goal” (Robbins and Judge, 2013). “While general motivation is concerned with an effort toward any goal, we’ll narrow the focus to organizational goals in order to reflect our singular interest in work-related behavior” (Robbins and Judge, 2013).
When we discuss motivation, we mean that it is a psychological action that is based on human needs. Therefore, motivation is
the process through which a person is inspired, directed, and sustained in their efforts to achieve a goal. In that context, energy might refer to a person's intensity, drive, or vitality. It may be the direction if someone is looking toward positive objectives. How long someone works to accomplish a goal is referred to as sustain or persistence. People's unmet wants come first in the motivating process, followed by a drive or incentive. Following the incentive, an effort is made to accomplish the goals set forth. So, this is how incentive works.
Extrinsic or intrinsic motivation is possible. You may motivate oneself intrinsically, whereas extrinsic motivation comes from other people. The degree of motivation varies between people and within people, as well as at different periods. People are far more driven to act when they have enormous wants. In addition, drive may occasionally be satisfied even though it will not always lead to satisfaction. Motivation theories come in two different varieties. Both content and process philosophies fall under this group of concepts.
Content View of Motivation
1. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Assumptions
·
Low order needs take priority.
·
The needs are satisfied in a sequence.
·
Satisfied needs no longer motivate
behavior.
Criticisms
·
Generalizability.
·
Only one need operates at one time.
1. 2. Alderfer’s ERG Theory
In
this theory, there can be more than one need seen at a one point. There are frustration regression principles
like Growth Needs, Relatedness Needs,
Existence Needs.
2. 3. McClelland’s Need Theory
There
3 needs for motivation. Those are,
· Need
for Achievement
· Need
for Power
· Need
for Affiliation
1 2. Douglas
Mc. Gregory’s XY Theory
Theory
X
The
assumption that employees dislike work, are lazy, dislike responsibility and
must be coerced to perform.
Theory
Y
The
assumption that employees like work, are creative, seek responsibility and can
exercise self-direction.
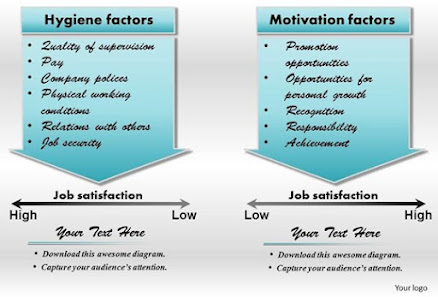
3. Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
Process View of
Motivation
1. 1. Goal
Setting Theory
Specific
goals increase performance and when accepted the difficult goals result in
higher performance than do easy goals.
1. 2. Porter
& Lawler’s Expectancy Theory
In
this motivation depends on individual’s expectations and based on effort,
performance and outcome expectations. Also not concerned with identifying types
of needs but with the thinking process.
1. 3. Equity
Theory
Equity
theory focuses on individual’s perception of how fairly they are treated
compared with others. Motivation depends on social equity in the rewards they
expect for performance. Equity is an individual belief that compares with
other’s outcomes and job inputs.
1. 4. Reinforcement
Theory
Reinforcement
theory is a limited effects media model applicable within the realm of
communication. The theory generally states that people seek out and remember
information that provides cognitive support for their pre-existing attitudes
and beliefs.
These
are theories of motivation and motivation allows us to change behavior, develop
competencies, be creative, set goals, grow interests, make plans, develop
talents and boost engagement.
v
Conclusion
Productivity can be hampered or enhanced depending on how motivation is generated. Management needs to be aware that they are working with people, not robots, and that motivating people means giving them incentives to accomplish things they want to do.
References
Robbins, S.P. and Coulter, M. (2016). Management. Boston, Mass.: Pearson.
Robbins, S.P. and Judge, T.A. (2013). Organizational behavior. 15th ed. Boston: Pearson.
Turner, J.H., 1987. Toward a sociological theory of motivation. American Sociological Review, pp.15-27.
Taormina, R.J. and Gao, J.H., 2013. Maslow and the motivation hierarchy: Measuring satisfaction of the needs. The American journal of psychology, 126(2), pp.155-177.











Very attractive article Asanka, The blog article defines motivation as a process that includes three key elements: energy, direction, and persistence. While the author touches upon different types of motivation, including intrinsic and extrinsic, that's better if we can have critical analysis of the various theories of motivation and their practical implications.
ReplyDeleteOne of the most popular motivation theories is Maslow's hierarchy of needs, which states that individuals are motivated by a series of needs, ranging from physiological to self-actualization. Another theory, Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory, identifies factors that can either create job satisfaction or dissatisfaction, such as job security, salary, and working conditions.
A critical analysis of these theories suggests that while they have been widely studied and applied, they have their limitations. For example, Maslow's theory has been criticized for its lack of empirical support and oversimplification of human needs. Herzberg's theory, on the other hand, has been criticized for its focus on job factors that can lead to dissatisfaction, rather than motivation. So What are your argument with this?
I completely agree that Maslow's hierarchy of needs is one of the most popular motivation theories out there. It makes a lot of sense that individuals are driven by different needs, and that fulfilling these needs can lead to higher levels of motivation and satisfaction.
DeleteThis article creating a conductive work environment that promotes organizational success Asanka . Well, apart from the key to an organization's success, it's also the level of commitment, drive and energy that a company's workers bring to the role every day. Without it, companies experience reduced productivity, lower levels of output and it's likely that the company will fall short of reaching important goals too.
ReplyDeleteWhy is Employee Motivation Important? (+ How to Improve it)
Perkbox
https://www.perkbox.com › resources › blog › why-e.
Thanks for comments, Increased productivity: When employees are motivated, they are more likely to be engaged and focused on their work, which can lead to increased productivity. Better quality of work: Motivated employees tend to put more effort into their work, leading to higher quality outcomes. Reduced absenteeism and turnover: When employees are motivated, they are more likely to show up to work and less likely to quit their jobs.
DeleteGreat article Asanka! As you correctly note, motivation is a crucial aspect of employee relations and organizational success. Understanding the different theories of motivation, such as Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, Alderfer's ERG Theory, McClelland's Need Theory, and others, can help managers effectively inspire, direct, and sustain employees' efforts towards achieving organizational goals. It's important to recognize that motivation can come from intrinsic or extrinsic sources and that individuals have varying degrees of motivation at different times. By creating a motivating work environment and recognizing individual needs and expectations, management can boost productivity and engagement. Remember, employees are not robots, and motivation plays a significant role in shaping behaviour, creativity, goal-setting, and talent development. I like the fact you have added some useful infographics in your article.
ReplyDeleteI totally agree with your post. Motivation is key to organizational success. I think Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs theory is one of the most important theories of motivation. It explains that people have different needs, and these needs can be categorized into five levels. Understanding these needs and addressing them appropriately can help managers motivate employees effectively
DeleteThis post describes the theories related to Employee motivation from various authors.
ReplyDeleteShahzadi et al. (2014) posits that employee motivation to be the drive that pushes the employees to work hard and fulfil what their managers want by reflecting their energy levels, commitment and creativity.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts on Shahzadi et al.'s (2014) article. I agree that employee motivation is a crucial factor in driving their performance and fulfilling their managers' expectations. When employees are motivated, they tend to be more energized, committed, and creative in their work, which can translate into higher productivity and better outcomes for the organization as a whole
DeleteThis is a very valuable article for today's business world. The level of devotion, drive, and energy that a company's employees bring to the job every day is, in addition to other factors, the secret to the success of an organization. Without it, businesses endure decreased productivity, lower levels of output, and a higher likelihood that they will miss key objectives.
ReplyDeleteThe level of dedication, vigor, and innovation exhibited by a company's employees while they are at work is known as employee motivation. Due to the fact that not every task will be engaging, it can be challenging for many businesses to maintain and improve worker motivation. Businesses must therefore discover strategies to maintain staff engagement while also monitoring and fostering employee motivation.
Thank you for sharing your insights on the importance of employee devotion, drive, and energy in the success of an organization. I completely agree with you that these factors are crucial to achieving and exceeding business goals.
Delete